align (noun: alignment) To place or organize things in a patterned order, following an apparent line.
amoeba A single-celled microbe that catches food and moves about by extending fingerlike projections of a colorless material called protoplasm. Amoebas are either free-living in damp environments or they are parasites.
bacterium (pl. bacteria) A single-celled organism. These dwell nearly everywhere on Earth, from the bottom of the sea to inside of plants and animals.
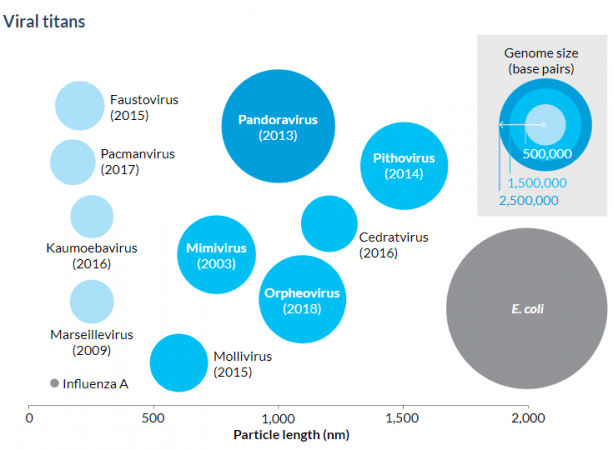
base pairs (in genetics) Sets of nucleotides that match up with each other on DNA or RNA. For DNA, adenine (A) matches up with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) matches up with guanine (G).
behemoth A term for anything that is amazingly big. The term comes from a monstrous animal described in the Bible’s book of Job.
DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid) A long, double-stranded and spiral-shaped molecule inside most living cells that carries genetic instructions. It is built on a backbone of phosphorus, oxygen, and carbon atoms. In all living things, from plants and animals to microbes, these instructions tell cells which molecules to make.
E. coli (short for Escherichia coli) A common bacterium that researchers often harness to study genetics. Some naturally occurring strains of this microbe cause disease, but many others do not.
genetic Having to do with chromosomes, DNA and the genes contained within DNA. The field of science dealing with these biological instructions is known as genetics. People who work in this field are geneticists.
genome The complete set of genes or genetic material in a cell or an organism. The study of this genetic inheritance housed within cells is known as genomics.
influenza (also known as flu) A highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory passages causing fever and severe aching. It often occurs as an epidemic.
microbiology The study of microorganisms, principally bacteria, fungi and viruses. Scientists who study microbes and the infections they can cause or ways that they can interact with their environment are known as microbiologists.
particle A minute amount of something.
prey (n.) Animal species eaten by others. (v.) To attack and eat another species.
range (in math or for measurements) The extent to which variation in values is possible. Also, the distance within which something can be reached or perceived.
RNA A molecule that helps “read” the genetic information contained in DNA. A cell’s molecular machinery reads DNA to create RNA, and then reads RNA to create proteins.
spherical Adjective for something that is round (as a sphere).
titan The term for any gigantic being. The term comes from Greek mythology. The six sons and six daughters of the Greek gods Uranus and Gaea were known as titans. Capitalized Titan is a moon of Saturn.
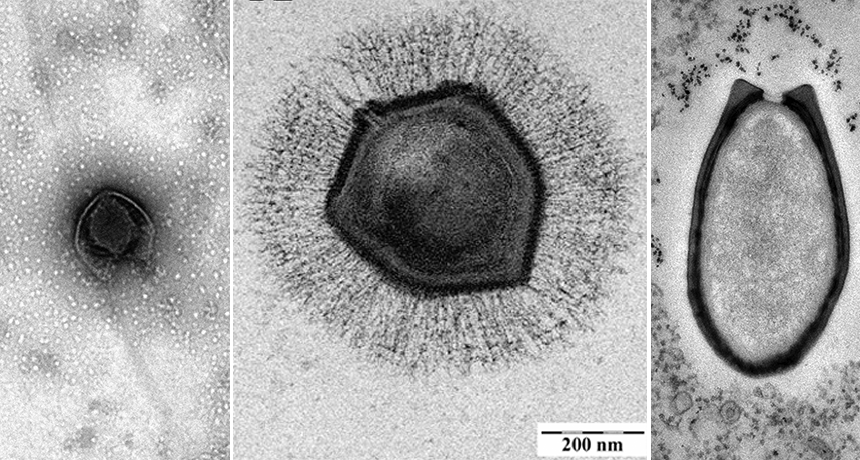
virus Tiny infectious particles consisting of RNA or DNA surrounded by protein. Viruses can reproduce only by injecting their genetic material into the cells of living creatures. Although scientists frequently refer to viruses as live or dead, in fact no virus is truly alive. It doesn’t eat like animals do, or make its own food the way plants do. It must hijack the cellular machinery of a living cell in order to survive.