Drug-resistant germs kill some 35,000 Americans each year
A government report adds two new germs to its list of urgent threats
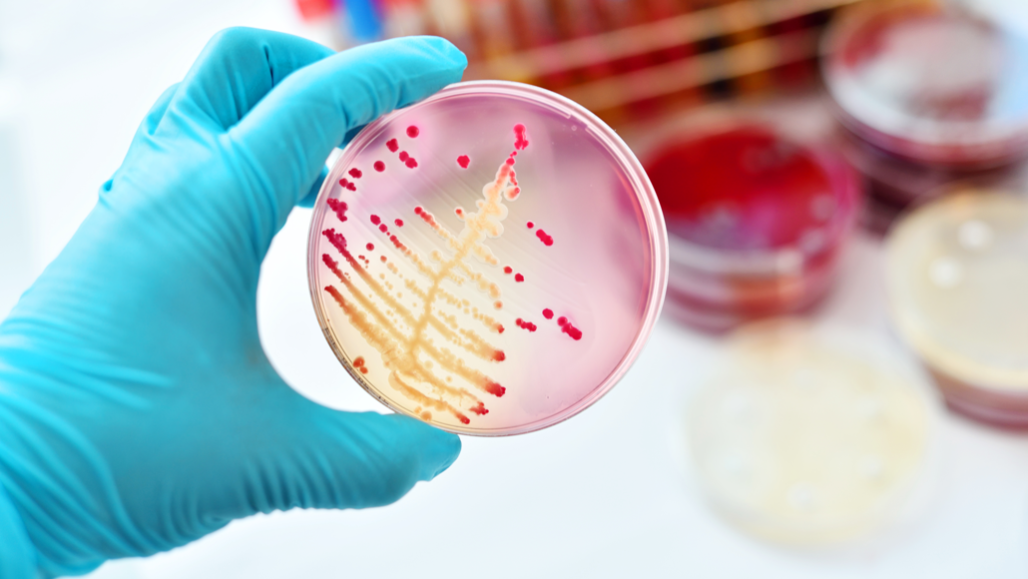
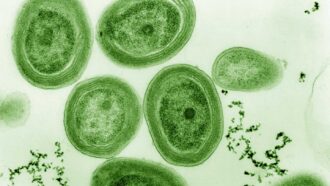
Researchers and infectious-disease experts can take swabs of germs from the nose or other places on a patient and then grow germs up in Petri dishes, as here. Afterward, they can treat the germs with antibiotics to see if they die — or resist them and live.
jarun011/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Each year, in the United States, infections that resist treatment with drugs sicken nearly 3 million people. Of these, some 35,000 die. That’s the finding of a new report.
Medicines have been developed to kill bacteria and fungi. These drugs are known as antimicrobials. But many strains of the wily germs have evolved. They can now survive these drugs. This is known as antibiotic resistance.
“The modern medicine available to us today may very well be gone tomorrow if we don’t slow the development of antibiotic resistance,” said Robert Redfield. He directs the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or CDC, in Atlanta, Ga. Redfield spoke at a news briefing on November 13.
The new report is CDC’s first update on drug-resistant infections since 2013. It used newly available data. These include electronic health records from more than 700 hospitals. Back in 2013, CDC estimated that some 23,000 Americans died from drug-resistant germs each year. CDC now thinks that estimate was low. A better number for 2013 would be around 44,000, it now says.
That number is close to 20 percent higher than the current rate. So there has been progress in cutting the spread of these infections. A large number of people pick up these germs in the hospital. So hospitals worked hard to slow the spread of these germs, noted Michael Craig during the news briefing. He’s a senior advisor on drug-resistant microbes at the CDC.
CDC cautions, however, that even its new numbers may not be accurate. They may be too low. In a letter published last January in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Mo., came up with far higher numbers. They had used different methods to make their estimates. They calculated that more than 150,000 people died from drug-resistant germs in 2010.
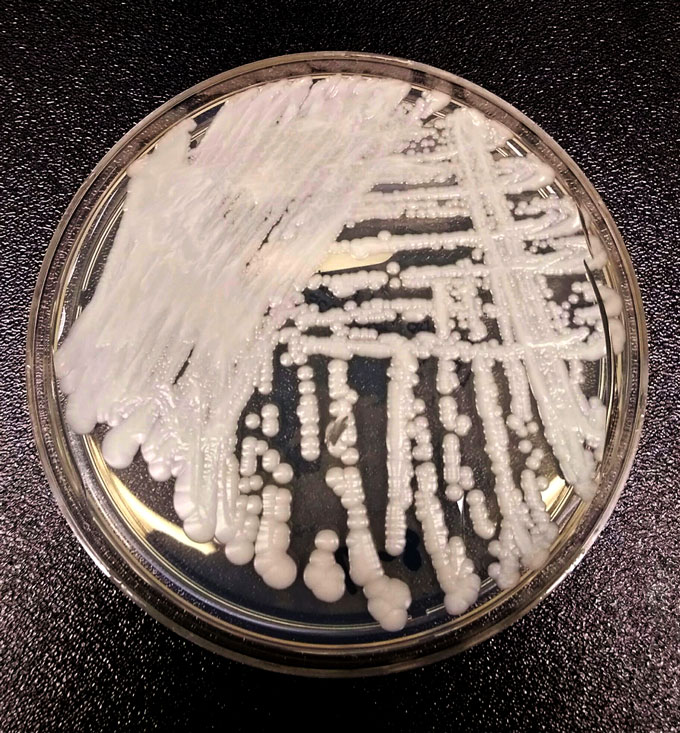
“The CDC’s new numbers represent excellent progress in assessing the burden of antibiotic resistance,” says Greg Frank. He directs infectious-disease policy for the Biotechnology Innovation Organization. This industry group is based in Washington, D.C. CDC’s numbers still likely underestimate the vast impact of drug-resistant germs, Frank says. Deaths due to these microbes often go underreported, he notes. One reason is that many people infected with these germs have other health issues, too. And those other issues, he explains, may be listed as the cause of death.
CDC’s new report adds two new drug-resistant microbes to the list that it considers urgent public health threats. One is a fungus. Known as Candida auris (Kan-DEE-duh AUR-is), it can resist drugs used to kill fungi. The other is a bacterium. Called Acinetobacter (Ah-SIN-ih-toh-BAK-tur), it can survive exposure to the antibiotic carbapenem.
Acinetobacter spreads mainly in health care facilities. It causes pneumonia and urinary-tract infections. C. auris also tends to strike people while they’re in the hospital. Says Craig, back when the last CDC report came out in 2013, “we didn’t even know about [C. auris].” Over the past six years, he notes, this germ “has circumnavigated the globe.” In its wake, he says, it left “a lot of infections and deaths.” Its quick rise from a medically unknown fungus to worldwide health threat may be due to climate change. That’s according to a report that came out this past July.