acid A chemical that increases the level of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Acids have a pH of between 0 and 7. Vinegar is made from acetic acid. Citrus fruits contain an acid known as citric acid.
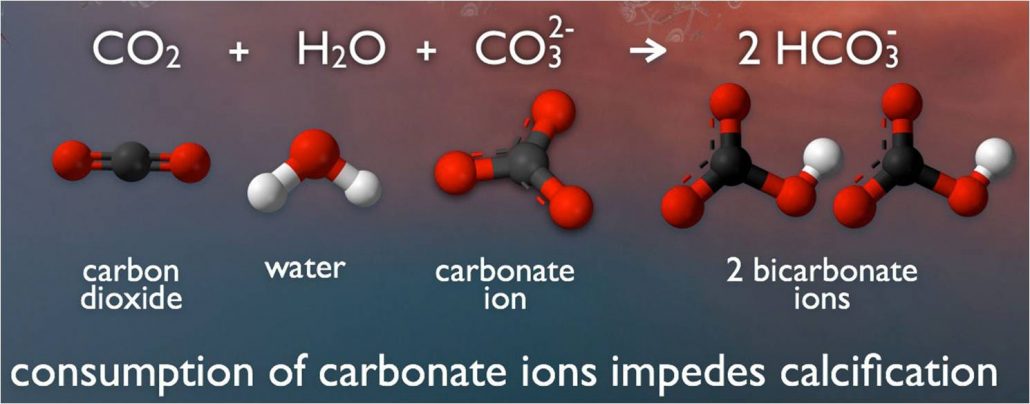
acidification The process of becoming more acidic. In the ocean, acidification occurs when seawater absorbs carbon dioxide. This triggers chemical reactions that reduce not only the pH of that water, but also the concentration of calcium carbonate, a mineral that many sea creatures use in making their shells.
base On a pH scale, bases are alkaline materials that have a pH of between 7 and 14. What makes them alkaline is the presence of hydroxide ions (OH-).
calcium carbonate The main chemical compound in limestone, a rock made from the tiny shells of ancient marine organisms. Its formula is CaCO3 (meaning it contains one calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms).
carbon dioxide A gas produced by all animals when the oxygen they inhale reacts with the carbon-rich foods that they’ve eaten. This colorless, odorless gas also is released when organic matter (including fossil fuels like oil or gas) is burned. Carbon dioxide acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat in Earth’s atmosphere. Plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen during photosynthesis, the process they use to make their own food.
distilled (as in water) Boiling a liquid, such as water, then allowing it to later condense from the steam. This process can be used to remove impurities in the starting material.
gauge A device to measure the size or volume of something. For instance, tide gauges track the ever-changing height of coastal water levels throughout the day. Or any system or event that can be used to estimate the size or magnitude of something else. (v. to gauge) The act of measuring or estimating the size of something.
global warming The gradual increase in the overall temperature of Earth’s atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect. This effect is caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons and other gases in the air, many of them released by human activity.
greenhouse effect A greenhouse is a building made of glass. As sunlight streams through the windows, it turns into heat, which becomes trapped inside. Because many gases in Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, scientists have come to call the phenomenon the “greenhouse effect.” Although the greenhouse effect works somewhat differently from an actual greenhouse, the name stuck anyway.
greenhouse gas A gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing heat. Carbon dioxide is one example of a greenhouse gas.
Industrial Revolution A period of time around 1750 that was marked by new manufacturing processes and a switch from wood to coal and other fossil fuels as a main source of energy.