(for more about Power Words, click here)
broadcast To cast — or send out — something over a relatively large distance. A farmer may broadcast seeds by flinging them by hand over a large area. A loudspeaker may send sounds out over a great distance. An electronic transmitter may emit electromagnetic signals over the air to a distant radio, television or other receiving device. And a newscaster can broadcast details of events to listeners across a large area, even the world.
electromagnetic An adjective referring to light radiation, to magnetism or to both.
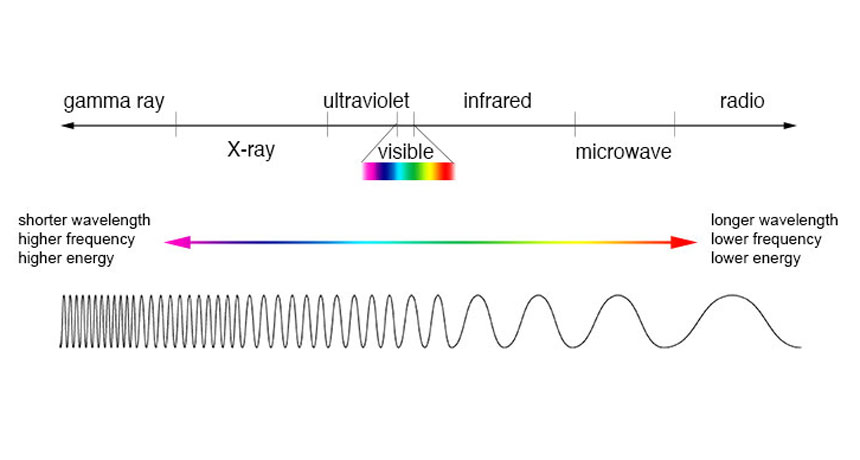
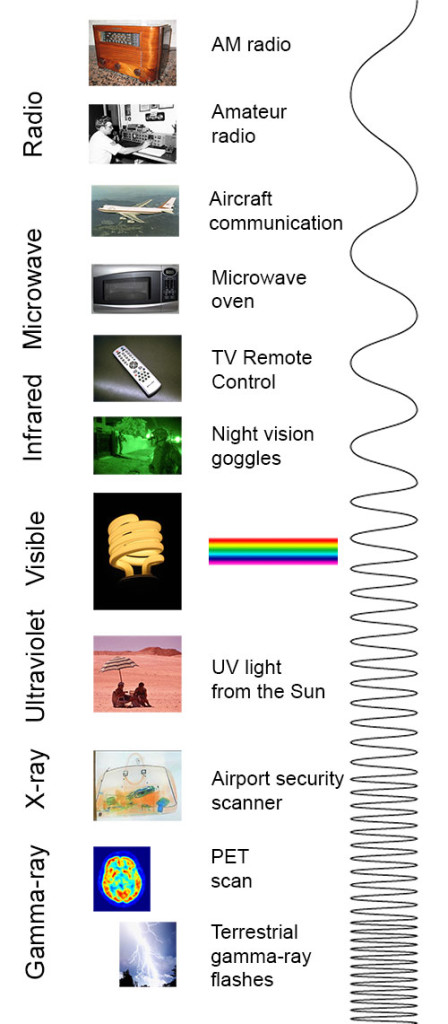
electromagnetic spectrum The range of radiation that spans from gamma- and X-rays through visible light and on to radio waves. Each type of radiation within the spectrum typically is classified by its wavelength.
frequency The number of times a specified periodic phenomenon occurs within a specified time interval. (In physics) The number of wavelengths that occurs over a particular interval of time.
gamma rays High-energy radiation often generated by processes in and around exploding stars. Gamma rays are the most energetic form of light.
hertz The frequency with which something (such as a wavelength) occurs, measured in the number of times the cycle repeats during each second of time.
inverse Something that is the opposite or reverse of another thing, or that moves in the opposite direction to something.
microwaves An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength shorter than that of normal radio waves but longer than those of infrared radiation (heat) and of visible light.
radiation (in physics) One of the three major ways that energy is transferred. (The other two are conduction and convection.) In radiation, electromagnetic waves carry energy from one place to another. Unlike conduction and convection, which need material to help transfer the energy, radiation can transfer energy across empty space.
radio waves Waves in a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are a type that people now use for long-distance communication. Longer than the waves of visible light, radio waves are used to transmit radio and television signals. They also are used in radar.
spectrum (plural: spectra) A range of related things that appear in some order. (in light and energy) The range of electromagnetic radiation types; they span from gamma rays to X rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared energy, microwaves and radio waves.
speed of light A constant often used in physics, corresponding to 1.08 billion kilometers (671 million miles) per hour.
ultraviolet A portion of the light spectrum that is close to violet but invisible to the human eye.
universe The entire cosmos: All things that exist throughout space and time. It has been expanding since its formation during an event known as the Big Bang, some 13.8 billion years ago (give or take a few hundred million years).
wavelength The distance between one peak and the next in a series of waves, or the distance between one trough and the next. Visible light — which, like all electromagnetic radiation, travels in waves — includes wavelengths between about 380 nanometers (violet) and about 740 nanometers (red). Radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light includes gamma rays, X-rays and ultraviolet light. Longer-wavelength radiation includes infrared light, microwaves and radio waves.
X-ray A type of radiation analogous to gamma rays, but having somewhat lower energy.