contract: To activate muscle by allowing filaments in the muscle cells to connect. The muscle becomes more rigid as a result. (in commerce) An agreement between two parties, such as to make a purchase or provide some service.
earthquake: A sudden and sometimes violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within Earth’s crust or of volcanic action.
force: Some outside influence that can change the motion of a body, hold bodies close to one another, or produce motion or stress in a stationary body.
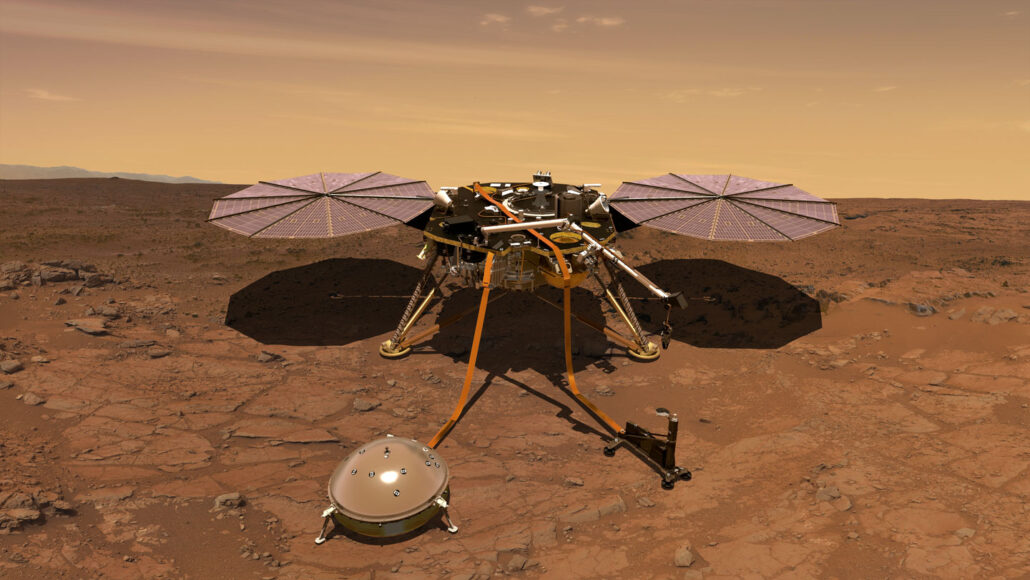
lander: A special, small vehicle designed to ferry humans or scientific equipment between a spacecraft and the celestial body they will explore.
magnitude: (in geology) A number used to describe the relative size of an earthquake. It runs from 1 to more than 8 and is calculated by the peak ground motion as recorded by seismographs. There are several magnitude scales. One of the more commonly used ones today is known as the moment magnitude. It’s based on the size of a fault (crack in Earth’s crust), how much the fault slips (moves) during a quake, and the energy force that was required to permit that movement. For each increase in magnitude, an earthquake produces 10 times more ground motion and releases about 32 times more energy. For perspective, a magnitude 8 quake can release energy equivalent to detonating 6 million tons of TNT. (in astronomy) A measure of a star brightness.
Mars: The fourth planet from the sun, just one planet out from Earth. Like Earth, it has seasons and moisture. But its diameter is only about half as big as Earth’s.
planet: A large celestial object that orbits a star but unlike a star does not generate any visible light.
propulsion: The act or process of driving something forward, using a force. For instance, jet engines are one source of propulsion used for keeping airplanes aloft.
Red Planet: A nickname for Mars.
seismic wave: A wave traveling through the ground produced by an earthquake or some other means.
seismometer: (also known as a seismograph ) An instrument that detects and measures tremors (known as seismic waves) as they pass through Earth.
wave: A disturbance or variation that travels through space and matter in a regular, oscillating fashion.