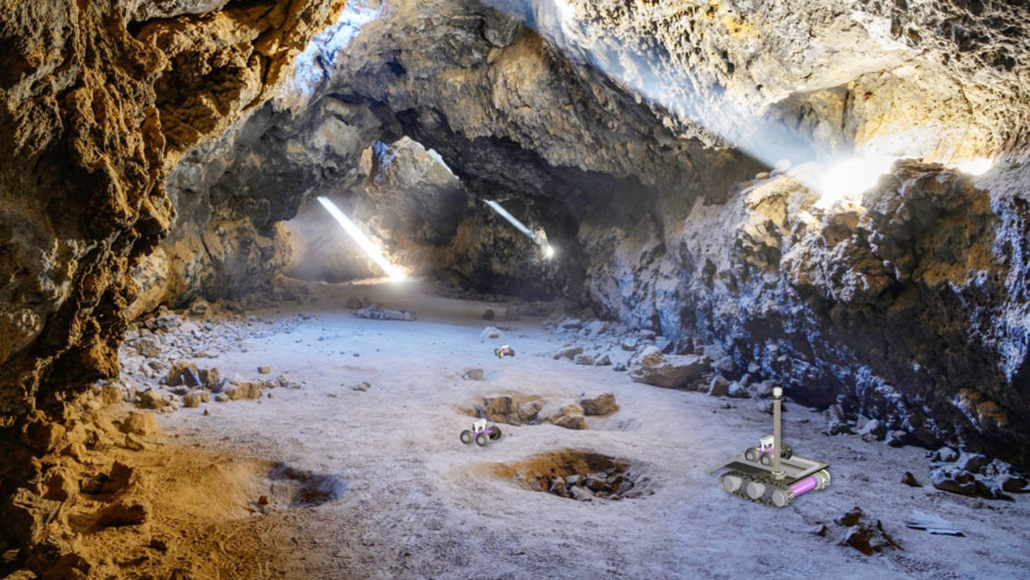
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
data: Facts and/or statistics collected together for analysis but not necessarily organized in a way that gives them meaning. For digital information (the type stored by computers), those data typically are numbers stored in a binary code, portrayed as strings of zeros and ones.
earthquake: A sudden and sometimes violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within Earth’s crust or of volcanic action.
exotic: An adjective to describe something that is highly unusual, strange or foreign (such as exotic plants).
forest: An area of land covered mostly with trees and other woody plants.
lava: Molten rock that comes up from the mantle, through Earth’s crust, and out of a volcano.
navigate: To find one’s way through a landscape using visual cues, sensory information (like scents), magnetic information (like an internal compass) or other techniques.
physicist: A scientist who studies the nature and properties of matter and energy.
planet: A large celestial object that orbits a star but unlike a star does not generate any visible light.
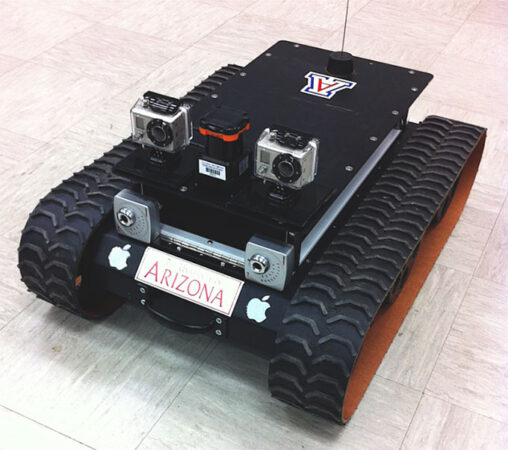
prototype: A first or early model of some device, system or product that still needs to be perfected.
sensor: A device that picks up information on physical or chemical conditions — such as temperature, barometric pressure, salinity, humidity, pH, light intensity or radiation — and stores or broadcasts that information. Scientists and engineers often rely on sensors to inform them of conditions that may change over time or that exist far from where a researcher can measure them directly.
strategy: A thoughtful and clever plan for achieving some difficult or challenging goal.
system: A network of parts that together work to achieve some function. For instance, the blood, vessels and heart are primary components of the human body's circulatory system. Similarly, trains, platforms, tracks, roadway signals and overpasses are among the potential components of a nation's railway system. System can even be applied to the processes or ideas that are part of some method or ordered set of procedures for getting a task done.
theoretical: An adjective for an analysis or assessment of something that based on pre-existing knowledge of how things behave. It is not based on experimental trials. Theoretical research tends to use math — usually performed by computers — to predict how or what will occur for some specified series of conditions. Experimental testing or observations of natural systems will then be needed to confirm what had been predicted.
Wi-Fi: A wireless technology that networks various electronic devices (such as cell phones and laptop computers); it allows them to share the same modem for Internet connections by using radio waves.