asteroid: A rocky object in orbit around the sun. Most asteroids orbit in a region that falls between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Astronomers refer to this region as the asteroid belt.
avian: Of or relating to birds.
birds: Warm-blooded animals with wings that first showed up during the time of the dinosaurs. Birds are jacketed in feathers and produce young from the eggs they deposit in some sort of nest. Most birds fly, but throughout history there have been the occasional species that don’t.
clade: The entire group of living and extinct species that all descend from some common ancient ancestor.
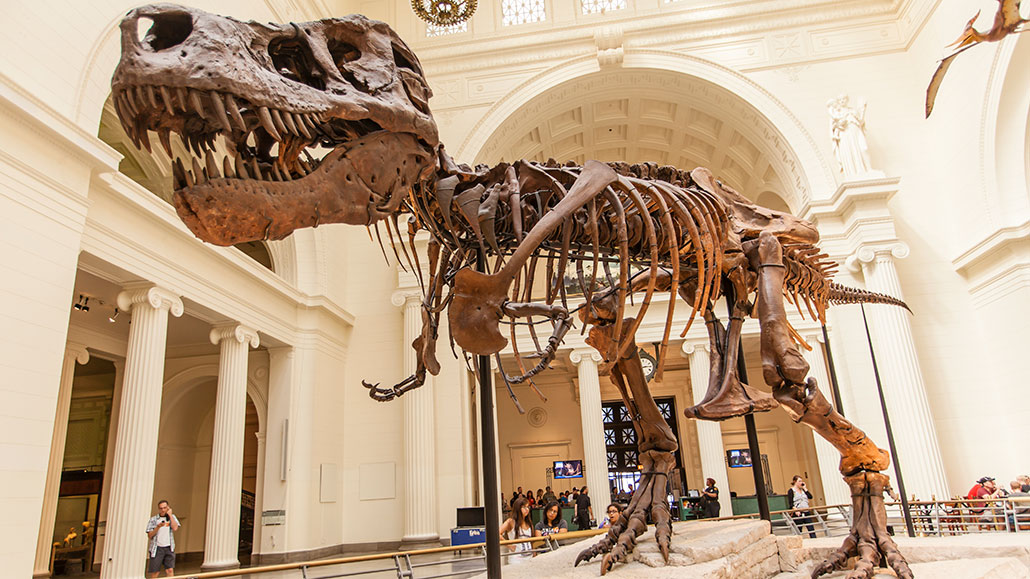
dinosaur: A term that means terrible lizard. These reptiles emerged around 243 million years ago. All descended from egg-laying reptiles known as archosaurs. Their descendants eventually split into two lines. For many decades, they have been distinguished by their hips. The lizard-hipped line are believed to have led to the saurischians, such as two-footed theropods like T. rex and the lumbering four-footed Apatosaurus (once known as brontosaurus). A second line of so-called bird-hipped, or ornithischian dinosaurs, appears to have led to a widely differing group of animals that included the stegosaurs and duckbilled dinosaurs. Many large dinosaurs died out around 66 million years ago. But some saurischians lived on and are now the birds we see today (and they now have a so-called “bird-hipped” pelvis).
egg: A reproductive cell that contains half of the genetic information necessary to form a complete organism. In humans and in many other animals, ovaries produce eggs. When an egg fuses with a sperm, they combine to produce a new cell, called a zygote. This is the first step in the development of a new organism."
extinct: An adjective that describes a species for which there are no living members.
fossil: Any preserved remains or traces of ancient life. There are many different types of fossils: The bones and other body parts of dinosaurs are called “body fossils.” Things like footprints are called “trace fossils.” Even specimens of dinosaur poop are fossils. The process of forming fossils is called fossilization.
Jurassic: Lasting from about 200 million to 145.5 million years ago, it’s the middle period of the Mesozoic Era. This was a time when dinosaurs were the dominant form of life on land.
lizard: A type of reptile that typically walks on four legs, has a scaly body and a long tapering tail. Unlike most reptiles, lizards also typically have movable eyelids. Examples of lizards include the tuatara, chameleons, Komodo dragon, and Gila monster.
ornithischians: One of the two major groups of dinosaurs, the other being the saurischians. Ornithischian hip bones were arranged like those of birds. Despite this similarity, ornithischians are not related to birds.
reptile: Cold-blooded vertebrate animals, whose skin is covered with scales or horny plates. Snakes, turtles, lizards and alligators are all reptiles.
saurischians: One of the two major groups of dinosaurs, the other being the ornithischians. Sauriscian hip bones are described as “lizard”-like, as the bones point forward the way a modern lizard’s do. Modern birds are saurischians.
species: A group of similar organisms capable of producing offspring that can survive and reproduce.
stegosaurs: Plant-eating dinosaurs that had large, protective plates or spikes on their backs and tails. The best known: stegosaurus, a 6 meter (20-foot) long creature from the late Jurassic that lumbered around the Earth some 150 million years ago.
Tyrannosaurus rex: A top-predator dinosaur that roamed Earth during the late Cretaceous period. Adults could be 12 meters (40 feet) long.