3-D: Short for three-dimensional. This term is an adjective for something that has features that can be described in three dimensions — height, width and length.
ancestor: A predecessor. It could be a family forebear, such as a parent, grandparent or great-great-great grandparent. Or it could be a species, genus, family or other order of organisms from which some later one evolved. For instance, ancient dinosaurs are the ancestors of today's birds. (antonym: descendant)
birds: Warm-blooded animals with wings that first showed up during the time of the dinosaurs. Birds are jacketed in feathers and produce young from the eggs they deposit in some sort of nest. Most birds fly, but throughout history there have been the occasional species that don’t.
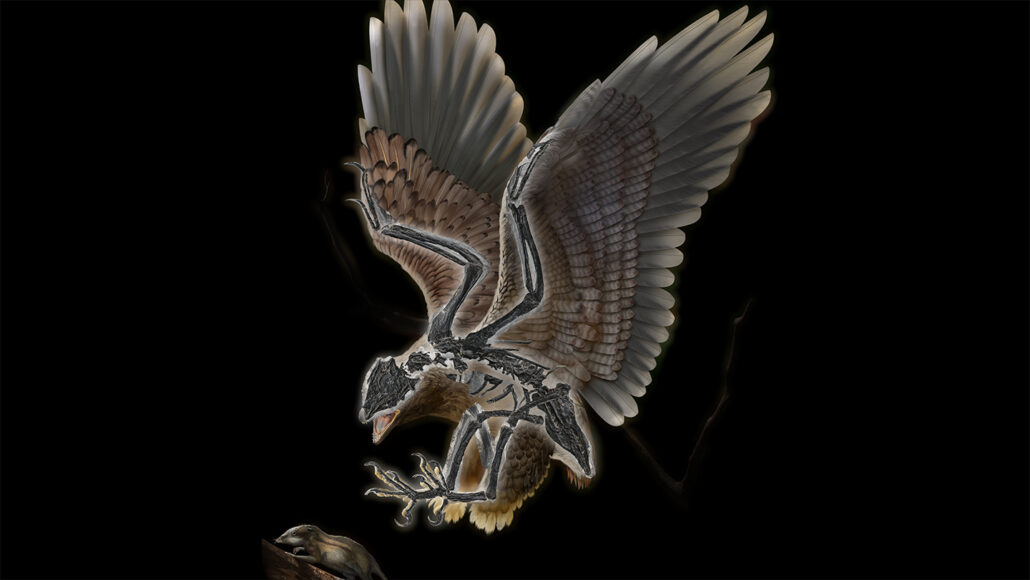
birds of prey: Birds, such as falcons and owl, that hunt for their food.
descendant: A blood relative of a person who lived during a previous time.
digit: A structure, like a finger or toe, at the end of the limbs of many vertebrates. (in math) An individual numeral (from 0 to 9) used to represent a number or some part of a number.
digital: (in computer science and engineering) An adjective indicating that something has been developed numerically on a computer or on some other electronic device, based on a binary system (where all numbers are displayed using a series of only zeros and ones).
dinosaur: A term that means terrible lizard. These reptiles emerged around 243 million years ago. All descended from egg-laying reptiles known as archosaurs. Their descendants eventually split into two lines. For many decades, they have been distinguished by their hips. The lizard-hipped line are believed to have led to the saurischians, such as two-footed theropods like T. rex and the lumbering four-footed Apatosaurus. A second line of so-called bird-hipped, or ornithischian dinosaurs, appears to have led to a widely differing group of animals that included the stegosaurs and duckbilled dinosaurs. Many large dinosaurs died out around 66 million years ago. But some saurischians lived on. They are now the birds we see today (and who have now evolved that so-called “bird-hipped” pelvis).
ecology: A branch of biology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings. A scientist who works in this field is called an ecologist.
evolution: (v. to evolve) A process by which species undergo changes over time, usually through genetic variation and natural selection. These changes usually result in a new type of organism better suited for its environment than the earlier type. The newer type is not necessarily more “advanced,” just better adapted to the particular conditions in which it developed. Or the term can refer to changes that occur as some natural progression within the non-living world (such as computer chips evolving to smaller devices which operate at an ever faster speed).
evolve: (adj. evolving) To change gradually over generations, or a long period of time. In living organisms, such an evolution usually involves random changes to genes that will then be passed along to an individual’s offspring. These can lead to new traits, such as altered coloration, new susceptibility to disease or protection from it, or different shaped features (such as legs, antennae, toes or internal organs). Nonliving things may also be described as evolving if they change over time. For instance, the miniaturization of computers is sometimes described as these devices evolving to smaller, more complex devices.
fossil: Any preserved remains or traces of ancient life. There are many different types of fossils: The bones and other body parts of dinosaurs are called “body fossils.” Things like footprints are called “trace fossils.” Even specimens of dinosaur poop are fossils. The process of forming fossils is called fossilization.
insect: A type of arthropod that as an adult will have six segmented legs and three body parts: a head, thorax and abdomen. There are hundreds of thousands of insects, which include bees, beetles, flies and moths.
lizard: A type of reptile that typically walks on four legs, has a scaly body and a long tapering tail. Unlike most reptiles, lizards also typically have movable eyelids. Examples of lizards include the tuatara, chameleons, Komodo dragon, and Gila monster.
model: A simulation of a real-world event (usually using a computer) that has been developed to predict one or more likely outcomes. Or an individual that is meant to display how something would work in or look on others.
muscle: A type of tissue used to produce movement by contracting its cells, known as muscle fibers. Muscle is rich in protein, which is why predatory species seek prey containing lots of this tissue.
paleontologist: A scientist who specializes in studying fossils, the remains of ancient organisms.
preen: To make oneself look more attractive, such as by combing one’s hair or straightening the wrinkles out of one’s clothes. (in biology) A verb for the way birds straighten and clean their feathers.
prey: (n.) Animal species eaten by others. (v.) To attack and eat another species.
skull: The skeleton of a person’s or animal’s head.
theropod: A usually meat-eating dinosaur that belonged to a group whose members are typically bipedal (walk on two legs). They range from small and delicately built to very large.
trove: A collection of valuable things.