arthropod: Any of numerous invertebrate animals of the phylum Arthropoda, including the insects, crustaceans, arachnids and myriapods, that are characterized by an exoskeleton made of a hard material called chitin and a segmented body to which jointed appendages are attached in pairs.
caveat: A potential exception to the general rule or to some general expectation.
entomologist: A biologist who specializes in the study of arthropods, such as insects.
fungi: (sing: fungus) Organisms with one or more cells that reproduce via spores and feed on living or decaying organic matter. Examples include mold, yeasts and mushrooms.
litter: (in biology) Decaying leaves and other plant matter on the surface of a forest floor.
microscope: An instrument used to view objects, like bacteria, or the single cells of plants or animals, that are too small to be visible to the unaided eye.
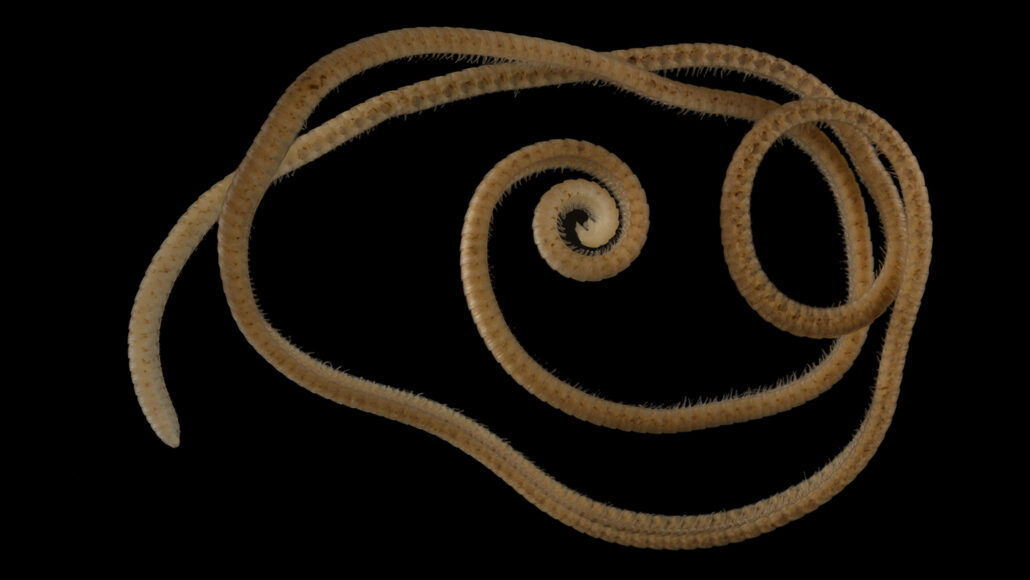
millipedes: Long-bodied plant-eating arthropods with many segments. Most body segments have two pairs of legs. Their nickname: thousand-leggers.
mineral: Crystal-forming substances that make up rock, such as quartz, apatite or various carbonates. Most rocks contain several different minerals mish-mashed together. A mineral usually is solid and stable at room temperatures and has a specific formula, or recipe (with atoms occurring in certain proportions) and a specific crystalline structure (meaning that its atoms are organized in regular three-dimensional patterns).
recall: To remember.
species: A group of similar organisms capable of producing offspring that can survive and reproduce.
subterranean: An adjective for something that is found or occurs below the ground’s surface.
trait: A characteristic feature of something. (in genetics) A quality or characteristic that can be inherited.