atmosphere: The envelope of gases surrounding Earth, another planet or a moon.
average: (in science) A term for the arithmetic mean, which is the sum of a group of numbers that is then divided by the size of the group.
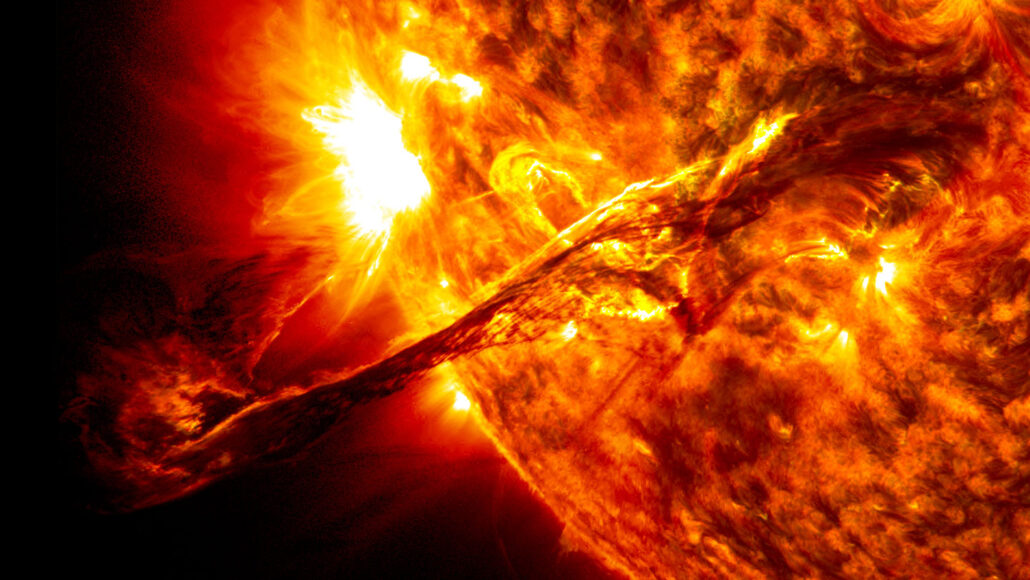
coronal mass ejections: The powerful release of huge bubbles of gas threaded with magnetic field lines. These can be spew from the sun over a span of hours. They can accompany solar flares, but usually do not.
eclipse: This occurs when two celestial bodies line up in space so that one totally or partially obscures the other. In a solar eclipse, the sun, moon and Earth line up in that order. The moon casts its shadow on the Earth. From Earth, it looks like the moon is blocking out the sun. In a lunar eclipse, the three bodies line up in a different order — sun, Earth, moon — and the Earth casts its shadow on the moon, turning the moon a deep red.
field: (in physics) A region in space where certain physical effects operate, such as magnetism (created by a magnetic field), gravity (by a gravitational field), mass (by a Higgs field) or electricity (by an electrical field).
grid: (in electricity) The interconnected system of electricity lines that transport electrical power over long distances. In North America, this grid connects electrical generating stations and local communities throughout most of the continent.
magnet: A material that usually contains iron and whose atoms are arranged so they attract certain metals.
magnetic field: An area of influence created by certain materials, called magnets, or by the movement of electric charges.
magnetic field lines: The lines that surround a magnet (you can see this if you drop iron filings around the edges of a bar magnet).
mass: A number that shows how much an object resists speeding up and slowing down — basically a measure of how much matter that object is made from.
outage: (in energy) A term for a region that temporarily loses power (usually electric power) or the ability to operate.
plasma: (in chemistry and physics) A gaseous state of matter in which electrons separate from the atom. A plasma includes both positively and negatively charged particles.
satellite: A moon orbiting a planet or a vehicle or other manufactured object that orbits some celestial body in space.
solar: Having to do with the sun or the radiation it emits. It comes from sol, Latin for sun.
solar cycle: Sometimes referred to as the sunspot cycle, this is the roughly 11-year period during which the sun undergoes a host of changes as the star swings between periods of minimum and maximum activity. The number of sunspots changes (drops to near zero during the minimum). The magnetic field values at the solar surface also undergoes changes.
solar eclipse: An event in which the moon passes between the Earth and sun and obscures the sun, at least partially. In a total solar eclipse, the moon appears to cover the entire sun, revealing on the outer layer, the corona. If you were to view an eclipse from space, you would see the moon’s shadow traveling in a line across the surface of the Earth.
solar flare: An explosive event that takes place on the sun when energy that has built up in 'twisted' magnetic fields (usually above sunspots) becomes suddenly released. The energy can in minutes heat to many millions of degrees, emitting a burst of energy. That energy consists of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum, from gamma rays to radio waves.
star: The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become hot enough, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
sunspot: A spot or patch appearing from time to time on the sun’s surface, appearing dark by contrast with its surroundings.
technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry — or the devices, processes and systems that result from those efforts.